mirror of https://github.com/MISP/MISP
chg: [docs] correlation rework article added
parent
71d4e2cd10
commit
f8c27c86b5
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
|||
# MISP 2.4.160 - Correlation engine rework
|
||||
|
||||
With the latest release of MISP, we have completely redone how we do correlations. Why we did all of this, how you can switch to the new engines as well as what sort of functionalities will be at your disposal are the topics that this blog post is meant to discuss, so grab a summer drink of your choice, kick back and let's dive into it!
|
||||
|
||||
# Why did we have to retire the old engine?
|
||||
|
||||
Whilst the original correlation engine has worked for us well for over a decade, its design hinged on **correlations being a rarity**. Back when we started with MISP, we were dealing with tiny, governmental and military communities only, purely sharing targeted attack information. This meant that **correlations were rare** and an **immediate prompt for further investigation**.
|
||||
|
||||
Nowadays though, with the wealth of information we have access to, this phenomenon has shifted drastically. We're seeing different communities come together, share information that is relevant for different use-cases as well as often a natural duplication and overlap of analyses.
|
||||
|
||||
This recently lead to a great number of instances see their correlations explosively grow, reaching **several hundreds of Gigabytes in size on disk**, making instances unusable.
|
||||
|
||||
This lead us to rethink and to rework the way we do correlations.
|
||||
|
||||
# The new correlation engines
|
||||
|
||||
To resolve the above issue, we ended up reimplementing the engine - and realised that a lot of the processing burden when it comes to correlations, is a result of the access control checks governing MISP. This is crucial for any sharing community to be in place, in order to avoid information leakage through correlations.
|
||||
|
||||
With that said, a great many MISP instances are used internally within organisations, connected to sharing community instances. These instances normally only have a single organisation or team as user and therefore any data pulled down by the instance is visible to all of their users. In these cases, it would make sense to have an engine that avoids storing ACL information as well as utilising them for filtering when fetching correlations.
|
||||
|
||||
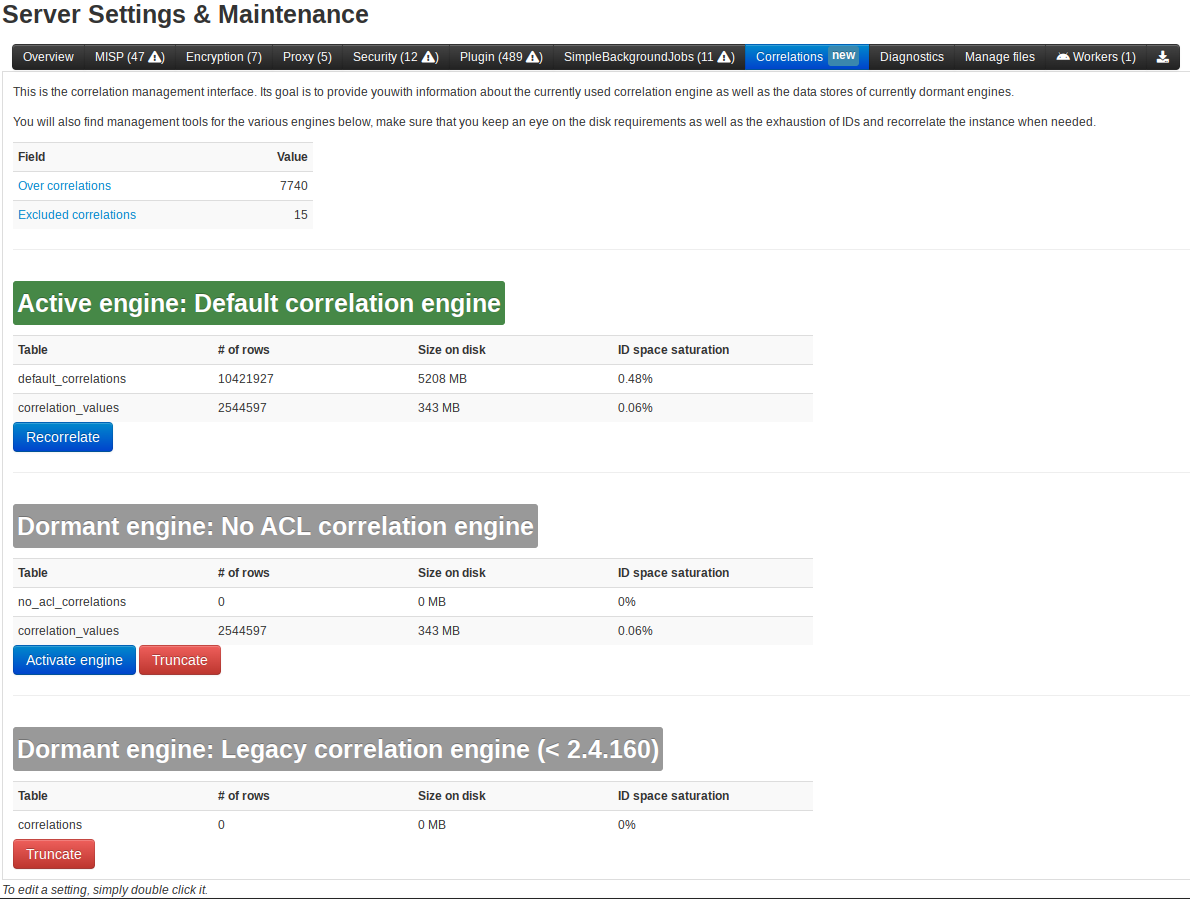
To accomodate both use-cases, we now have two correlation engines:
|
||||
|
||||
- The `Default correlation engine` - for sharing communities or for any instance with more than one organisation, where access control is crucial
|
||||
- The `No ACL correlation engine` - for internal, single organisation or "endpoint" MISP instances.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# The upgrade process
|
||||
|
||||
Upgrading to MISP 2.4.160 will automatically take care of everything required to get going with the new engines. The old correlation engine's data store is automatically purged (the table is truncated) and once the new table structures are created, a recorrelation job is started. Depending on the amount of data you have in your instance and your system performance, this might take quite a long time. For our largest operational instance it took 40 hours to recorrelate the data, so don't worry if you are not seeing the correlations immediately.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Default correlation engine` will be used by default, but feel free switch to the No ACL correlation engine if that fits your use-case more. You can reach the new correlation control center via Administration -> Server settings -> Correlations.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite the re-correlation potentially taking a long time, your instance will still be usable as usual during this time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Some precautions you can take to ease the process:
|
||||
|
||||
- Make sure that your mysql is able to perform well, it is especially important that the innodb_buffer_size is not using the rather restrictive default value
|
||||
- Potentially disalbe query caching as this is one of the situations where it can be quite detrimental due to the alternating high frequency reads/writes to the same table (you can do this by issuing the `SET GLOBAL query_cache_size = 0;` command via your MySQL CLI client)
|
||||
- Run multiple `default` background workers, since the correlation will keep one of the workers monitoring that queue busy for a prolonged period. (Add more via Administration->server settings->workers)
|
||||
|
||||
# How is the new engine different than the old one?
|
||||
|
||||
### A list of the main differences:
|
||||
|
||||
- Reworked data model
|
||||
- Correlation tables are purely made up of tinyint and int values - no more strings
|
||||
- All correlating values are spun off into a new table (`correlation_values`)
|
||||
- Correlation tables are now object ACL aware (this remedies a bug discovered in the old engine)
|
||||
- Correlation tables now contain the ACL data of both correlating entities, making them bi-directional
|
||||
- The bi-directional nature of the new correlation data model means that we only store each correlation ones rather than storing separate A->B and B->A entries
|
||||
- New over-correlation feature protects your instance from values that are generating overwhelmingly noisy correlation
|
||||
- Reworked logic for managing the correlations
|
||||
- In the case of the `No ACL correlation engine`, the datamodel is reduced to storing just the two correlating attribute and event IDs along with a reference to the correlating value.
|
||||
- Casualties of the new engines:
|
||||
- Proposal correlations have been sunset. They were of little use and were confusing due to their implementation
|
||||
- Rely on on-demand lookups for over-correlations
|
||||
|
||||
### Some of the expected outcomes
|
||||
- Massively increased performance
|
||||
- Reduced size on disk (size on disk reduced to 1-25%, depending on the data-sets used, based on our various community instances)
|
||||
- Some functionalities that were unusable prior to the release are suddenly low-cost, such as the correlation count on the index
|
||||
|
||||
### Issues to still resolve
|
||||
- Over-correlation table shows incorrect values for the number of correlating values (defaulting to the limit +1).
|
||||
- Some queries could still be tuned for some quick gains in performance
|
||||
|
||||
# Switching engines
|
||||
|
||||
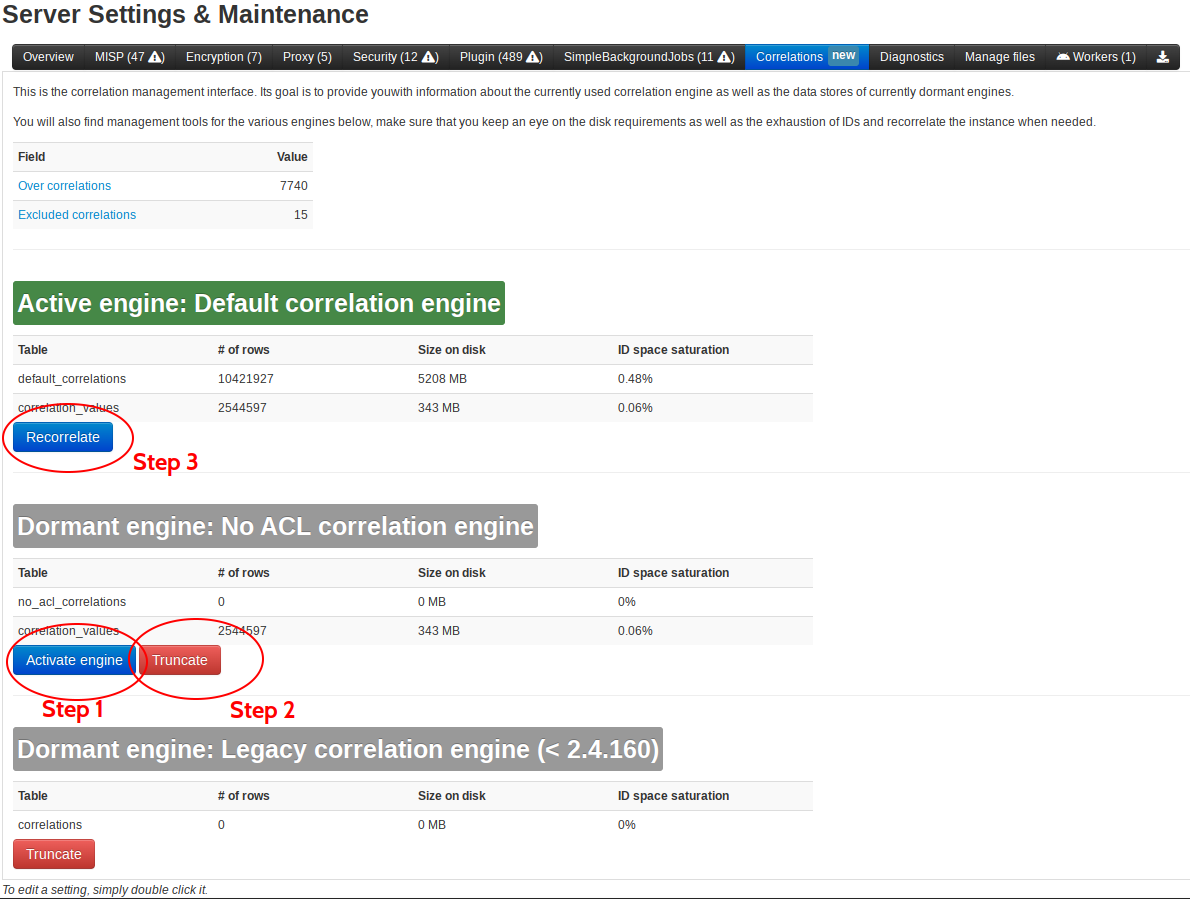
The following proedure is to be used to switch between the `Default correlation engine` and the `No ACL engine`:
|
||||
- Navigate to Administration -> server settings -> correlations
|
||||
- Click on `Activate` under the chosen engine's header
|
||||
- Once the desired engine becomes active, truncate the table of the previously used engine to regain the disk space
|
||||
- Click on Re-correlate to start the process of correlating the data using the new engine
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Correlation filter management
|
||||
|
||||
With the automatic and manual correlation filtering in place, we have two new systems to manage:
|
||||
|
||||
### Over-correlation protection
|
||||
|
||||
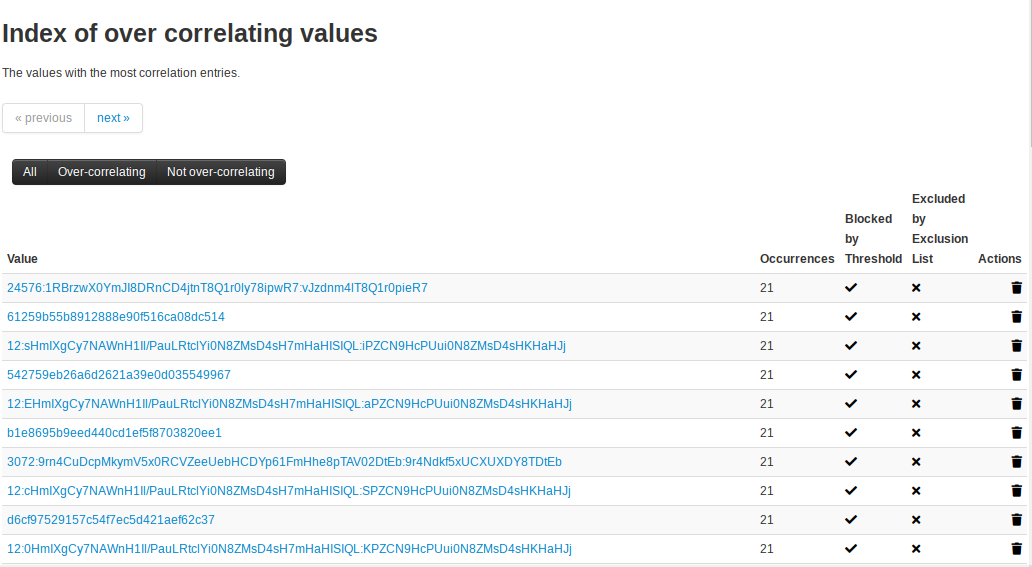
The new system will automatically restrict any correlations from being entered that would cross a given threshold. The data is stored in the database, via the `over_correlating_values` table and any correlation process will automatically add values to it.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the threshold allows for 20 correlating attributes with the same value, before it adds the value to the over correlation table and stops further correlations from being captured.
|
||||
|
||||
To view the values that are overcorrelating head over to administration -> over-correlating values.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
By clicking any of the values above, you will be redirected to the attribute search's results for the value, giving you a live result set.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the values being blocked based on the threshold the state of this table will also show whether a value has an exclusion entry in the Correlation exclusions system.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
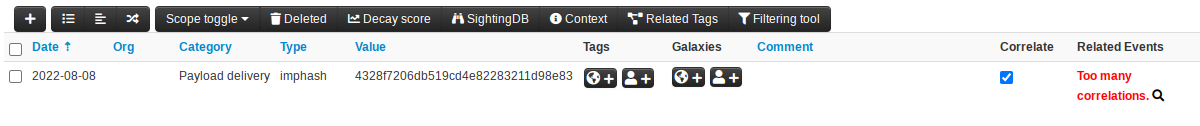
You will be able to see attrbutes as having too many correlations when viewing events, clicking on the magnifying glass will bring up the attribute search for the attribute value.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Correlation exclusions
|
||||
|
||||
This is the manual system that has existed for a few versions now in MISP. This system has been further improved and integrated into the event View.
|
||||
|
||||
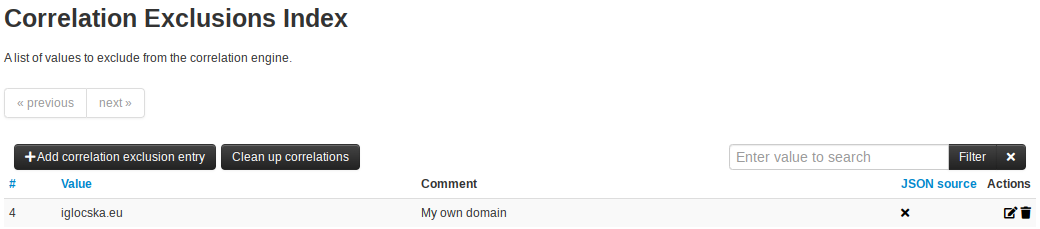
You can add new entries via the Over-correlation and the top correlations (Administration->top correlations) interfaces, as well as via the correlation exclusion index directly. You can also add an optional comment why you have excluded that value.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Add, update or remove entries directly in the correlation exclusion index (Accessible via the top correlations index - Administration -> Top Correlations and then clicking on correlation exclusions).
|
||||
|
||||
Any changes made are **NOT** actioned upon retroactively, until you run a "Clean up correlations" action.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
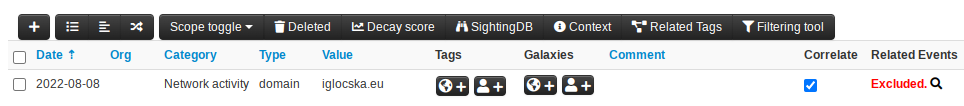
Events will show excluded correlations on the attributes directly, similarly to over-correlations. The main difference is the message, rather than `Too many correlations`, correlations will show up as `Excluded`.
|
||||
|
||||
# Engine development
|
||||
|
||||
The new engine system is built with modularity in mind, we expect to develop new engines in the future as well as see the community give life to custom engines.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently all generic correlation code (fetching data when correlating attributes, initiating processes) is handled by the Correlation model (`/app/Model/Correlation.php`) with custom engine implementations being available in the Behaviour directory (`/app/Model/Behavior/[correlation_name]CorrelationBehavior.php`).
|
||||
|
||||
For developers: All functions of the existing Correlation Behaviors that are public are **REQUIRED** by the system to be implemented in the engine.
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 23 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 23 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 93 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 68 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 25 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 141 KiB |
Loading…
Reference in New Issue