mirror of https://github.com/MISP/misp-galaxy
130 lines
4.9 KiB
Python
130 lines
4.9 KiB
Python
#!/usr/bin/python
|
|
|
|
from modules.galaxy import Galaxy
|
|
from modules.statistics import Statistics
|
|
|
|
import json
|
|
import os
|
|
import time
|
|
|
|
CLUSTER_PATH = "../../clusters"
|
|
SITE_PATH = "./site/docs"
|
|
GALAXY_PATH = "../../galaxies"
|
|
|
|
|
|
FILES_TO_IGNORE = [] # if you want to skip a specific cluster in the generation
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTRO = """
|
|
# MISP Galaxy
|
|
|
|
The MISP galaxy offers a streamlined approach for representing large entities, known as clusters, which can be linked to MISP events or attributes. Each cluster consists of one or more elements, represented as key-value pairs. MISP galaxy comes with a default knowledge base, encompassing areas like Threat Actors, Tools, Ransomware, and ATT&CK matrices. However, users have the flexibility to modify, update, replace, or share these elements according to their needs.
|
|
|
|
Clusters and vocabularies within MISP galaxy can be utilized in their original form or as a foundational knowledge base. The distribution settings for each cluster can be adjusted, allowing for either restricted or wide dissemination.
|
|
|
|
Additionally, MISP galaxies enable the representation of existing standards like the MITRE ATT&CK™ framework, as well as custom matrices.
|
|
|
|
The aim is to provide a core set of clusters for organizations embarking on analysis, which can be further tailored to include localized, private information or additional, shareable data.
|
|
|
|
Clusters serve as an open and freely accessible knowledge base, which can be utilized and expanded within [MISP](https://www.misp-project.org/) or other threat intelligence platforms.
|
|
|
|
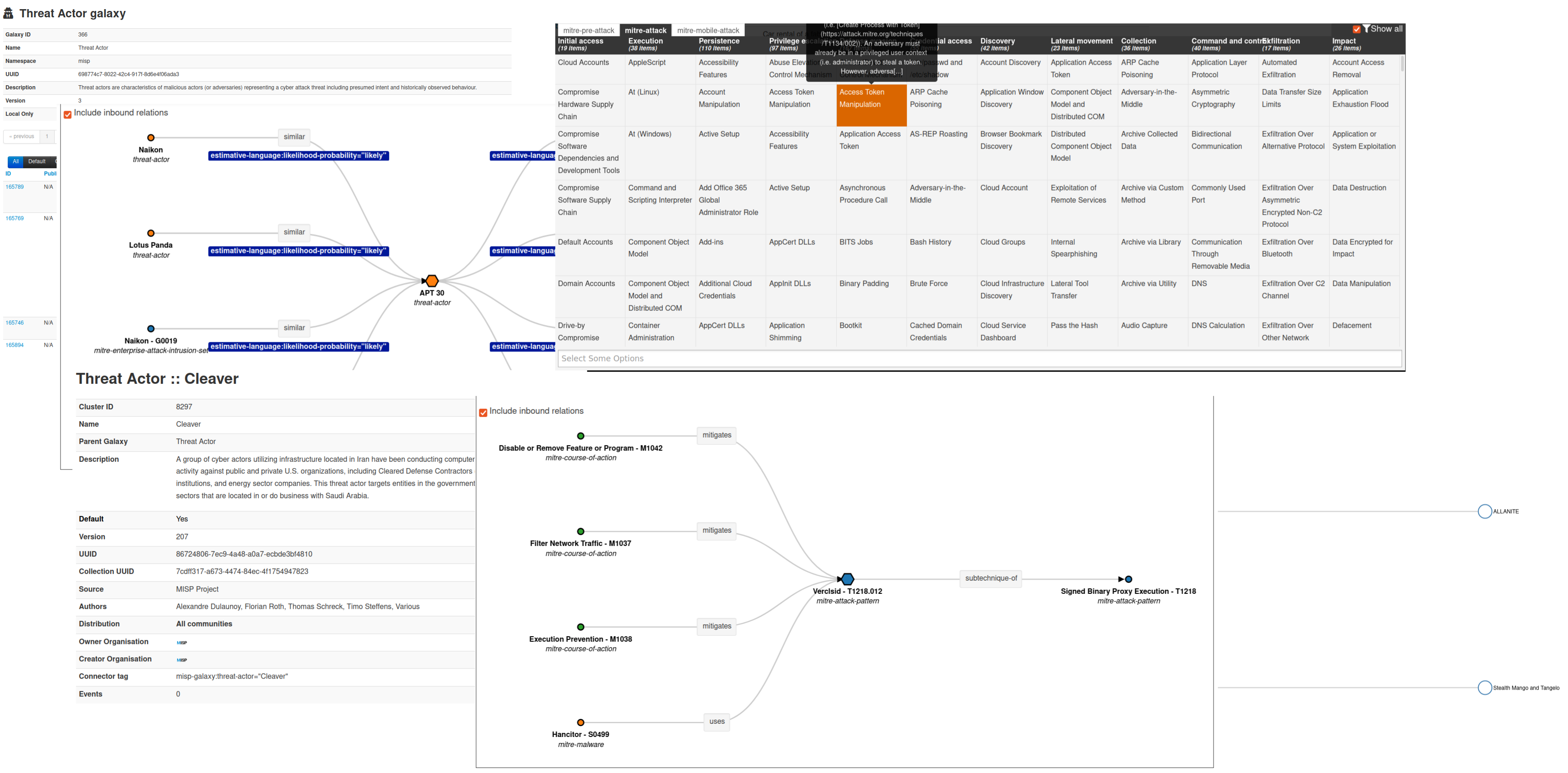
|
|
|
|
## Publicly available clusters
|
|
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
STATISTICS = """
|
|
## Statistics
|
|
|
|
You can find some statistics about MISP galaxies [here](./statistics.md).
|
|
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
CONTRIBUTING = """
|
|
|
|
# Contributing
|
|
|
|
In the dynamic realm of threat intelligence, a variety of models and approaches exist to systematically organize, categorize, and delineate threat actors, hazards, or activity groups. We embrace innovative methodologies for articulating threat intelligence. The galaxy model is particularly versatile, enabling you to leverage and integrate methodologies that you trust and are already utilizing within your organization or community.
|
|
|
|
We encourage collaboration and contributions to the [MISP Galaxy JSON files](https://github.com/MISP/misp-galaxy/). Feel free to fork the project, enhance existing elements or clusters, or introduce new ones. Your insights are valuable - share them with us through a pull-request.
|
|
|
|
"""
|
|
|
|
def write_galaxy_entry(galaxy, site_path, cluster_dict):
|
|
galaxy.write_entry(site_path, cluster_dict)
|
|
return f"Finished writing entry for {galaxy.name}"
|
|
|
|
def create_index(galaxies):
|
|
index_output = INTRO
|
|
for galaxy in galaxies:
|
|
index_output += f"- [{galaxy.name}](./{galaxy.json_file_name}/index.md)\n"
|
|
index_output += STATISTICS
|
|
index_output += CONTRIBUTING
|
|
return index_output
|
|
|
|
|
|
def get_deprecated_galaxy_files():
|
|
deprecated_galaxy_files = []
|
|
for f in os.listdir(GALAXY_PATH):
|
|
with open(os.path.join(GALAXY_PATH, f)) as fr:
|
|
galaxy_json = json.load(fr)
|
|
if "namespace" in galaxy_json and galaxy_json["namespace"] == "deprecated":
|
|
deprecated_galaxy_files.append(f)
|
|
|
|
return deprecated_galaxy_files
|
|
|
|
|
|
def main():
|
|
start_time = time.time()
|
|
|
|
FILES_TO_IGNORE.extend(get_deprecated_galaxy_files())
|
|
galaxies_fnames = []
|
|
for f in os.listdir(CLUSTER_PATH):
|
|
if ".json" in f and f not in FILES_TO_IGNORE:
|
|
galaxies_fnames.append(f)
|
|
galaxies_fnames.sort()
|
|
|
|
galaxies = []
|
|
for galaxy in galaxies_fnames:
|
|
with open(os.path.join(CLUSTER_PATH, galaxy)) as fr:
|
|
galaxy_json = json.load(fr)
|
|
galaxies.append(
|
|
Galaxy(
|
|
cluster_list=galaxy_json["values"],
|
|
authors=galaxy_json["authors"],
|
|
description=galaxy_json["description"],
|
|
name=galaxy_json["name"],
|
|
json_file_name=galaxy.split(".")[0],
|
|
)
|
|
)
|
|
cluster_dict = {}
|
|
for galaxy in galaxies:
|
|
for cluster in galaxy.clusters:
|
|
cluster_dict[cluster.uuid] = cluster
|
|
|
|
statistics = Statistics(cluster_dict=cluster_dict)
|
|
for galaxy in galaxies:
|
|
for cluster in galaxy.clusters:
|
|
statistics.add_cluster(cluster)
|
|
|
|
# Write files
|
|
if not os.path.exists(SITE_PATH):
|
|
os.mkdir(SITE_PATH)
|
|
|
|
for galaxy in galaxies:
|
|
galaxy.write_entry(SITE_PATH, cluster_dict)
|
|
|
|
index_output = create_index(galaxies)
|
|
|
|
statistics.write_entry(SITE_PATH)
|
|
|
|
with open(os.path.join(SITE_PATH, "index.md"), "w") as index:
|
|
index.write(index_output)
|
|
|
|
print(f"Finished file creation in {time.time() - start_time} seconds")
|
|
|
|
|
|
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
|
main()
|