|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| admiralty-scale | ||
| adversary | ||
| circl | ||
| de-vs | ||
| dni-ism | ||
| ecsirt | ||
| eu-critical-sectors | ||
| euci | ||
| first_csirt_case_classification | ||
| fr-classification | ||
| malware | ||
| nato | ||
| osint | ||
| tlp | ||
| tools | ||
| veris | ||
| README.md | ||
README.md
MISP Taxonomies
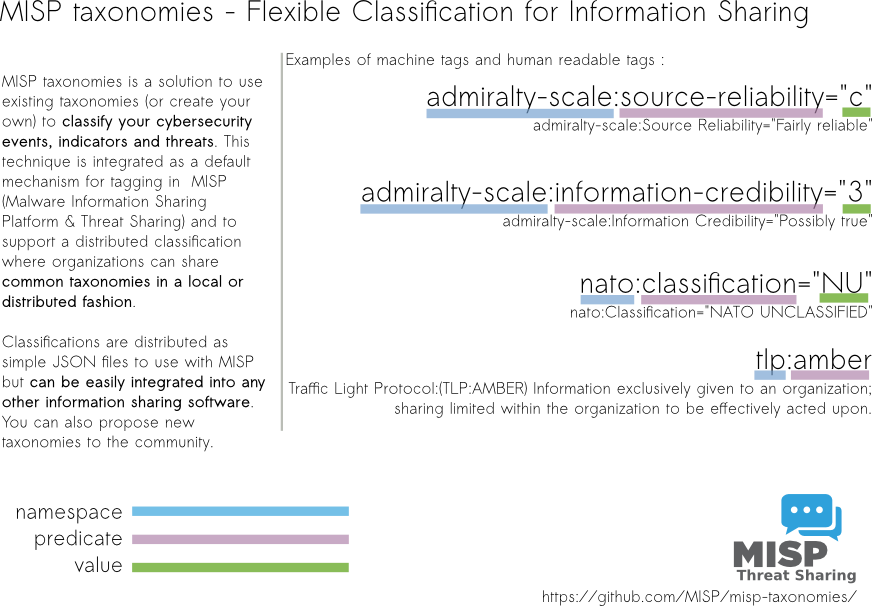
Taxonomies that can be used in MISP (2.4) and other information sharing tool and expressed in Machine Tags (Triple Tags). A machine tag is composed of a namespace (MUST), a predicate (MUST) and an (OPTIONAL) value. Machine tags are often called triple tag due to their format.
The following taxonomies can be used in MISP (as local or distributed tags) or in other tools willing to share common taxonomies among security information sharing tools.
The following taxonomies are described:
- Admiralty Scale
- CIRCL Taxonomy - Schemes of Classification in Incident Response and Detection
- DE German (DE) Government classification markings (VS)
- eCSIRT and IntelMQ incident classification
- EUCI - EU classified information marking
- FIRST CSIRT Case classification
- Information Security Marking Metadata from DNI (Director of National Intelligence - US)
- Malware classification based on a SANS document
- NATO Classification Marking
- OSINT Open Source Intelligence - Classification
- TLP - Traffic Light Protocol
- Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing VERIS
Admiralty Scale
The Admiralty Scale (also called the NATO System) is used to rank the reliability of a source and the credibility of an information.
CIRCL Taxonomy - Schemes of Classification in Incident Response and Detection
CIRCL Taxonomy is a simple scheme for incident classification and area topic where the incident took place.
DE German (DE) Government classification markings (VS)
Taxonomy for the handling of protectively marked information in MISP with German (DE) Government classification markings (VS).
eCSIRT and IntelMQ incident classification
eCSIRT incident classification Appendix C of the eCSIRT EU project including IntelMQ updates.
EUCI classification
EU classified information (EUCI) means any information or material designated by a EU security classification, the unauthorised disclosure of which could cause varying degrees of prejudice to the interests of the European Union or of one or more of the Member States as described.
FIRST CSIRT Case classification
FIRST CSIRT Case Classification.
Information Security Marking Metadata DNI (Director of National Intelligence - US)
ISM (Information Security Marking Metadata) V13 as described by DNI.gov.
Malware classification
Malware classification based on a SANS whitepaper about malware.
NATO Classification Marking
Marking of Classified and Unclassified materials as described by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO.
TLP - Traffic Light Protocol
The Traffic Light Protocol - or short: TLP - was designed with the objective to create a favorable classification scheme for sharing sensitive information while keeping the control over its distribution at the same time.
Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing VERIS
Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing is a format created by the VERIS community.
How to contribute your taxonomy?
It is quite easy. Create a JSON file describing your taxonomy as triple tags (e.g. check an existing one like Admiralty Scale), create a directory matching your name space, put your machinetag file in the directory and pull your request. That's it. Everyone can benefit from your taxonomy and can be automatically enabled in information sharing tools like MISP.
How to add your private taxonomy to MISP
$ cd /var/www/MISP/app/files/taxonomies/
$ mkdir privatetaxonomy
$ vi machinetag.json
Create a JSON file Create a JSON file describing your taxonomy as triple tags.
Once you are happy with your file go to MISP Web GUI taxonomies/index and update the taxonomies, the newly created taxonomy should be visible, now you need to activate the tags within your taxonomy.
MISP Taxonomies - tools
machinetag.py is a parsing tool to dump taxonomies expressed in Machine Tags (Triple Tags) and list all valid tags from a specific taxonomy.
% cd tools
% python machinetag.py
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="a"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="b"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="c"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="d"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="e"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="f"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="1"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="2"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="3"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="4"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="5"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="6"
...