Updates from Freddy |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github/workflows | ||
| CERT-XLM | ||
| DFRLab-dichotomies-of-disinformation | ||
| DML | ||
| PAP | ||
| access-method | ||
| accessnow | ||
| action-taken | ||
| admiralty-scale | ||
| adversary | ||
| ais-marking | ||
| analyst-assessment | ||
| approved-category-of-action | ||
| binary-class | ||
| cccs | ||
| circl | ||
| coa | ||
| collaborative-intelligence | ||
| common-taxonomy | ||
| copine-scale | ||
| course-of-action | ||
| cryptocurrency-threat | ||
| csirt-americas | ||
| csirt_case_classification | ||
| cssa | ||
| current-event | ||
| cyber-threat-framework | ||
| cycat | ||
| cytomic-orion | ||
| dark-web | ||
| data-classification | ||
| dcso-sharing | ||
| ddos | ||
| de-vs | ||
| dhs-ciip-sectors | ||
| diamond-model | ||
| dni-ism | ||
| domain-abuse | ||
| drugs | ||
| economical-impact | ||
| ecsirt | ||
| enisa | ||
| estimative-language | ||
| eu-marketop-and-publicadmin | ||
| eu-nis-sector-and-subsectors | ||
| euci | ||
| europol-event | ||
| europol-incident | ||
| event-assessment | ||
| event-classification | ||
| exercise | ||
| extended-event | ||
| failure-mode-in-machine-learning | ||
| false-positive | ||
| file-type | ||
| flesch-reading-ease | ||
| fpf | ||
| fr-classif | ||
| gdpr | ||
| gea-nz-activities | ||
| gea-nz-entities | ||
| gea-nz-motivators | ||
| gsma-attack-category | ||
| gsma-fraud | ||
| gsma-network-technology | ||
| honeypot-basic | ||
| ics | ||
| iep | ||
| iep2-policy | ||
| iep2-reference | ||
| ifx-vetting | ||
| incident-disposition | ||
| infoleak | ||
| information-security-data-source | ||
| information-security-indicators | ||
| interception-method | ||
| iot | ||
| kill-chain | ||
| maec-delivery-vectors | ||
| maec-malware-behavior | ||
| maec-malware-capabilities | ||
| maec-malware-obfuscation-methods | ||
| malware_classification | ||
| mapping | ||
| misinformation-website-label | ||
| misp | ||
| monarc-threat | ||
| ms-caro-malware | ||
| ms-caro-malware-full | ||
| mwdb | ||
| nato | ||
| nis | ||
| open_threat | ||
| osint | ||
| pandemic | ||
| passivetotal | ||
| pentest | ||
| phishing | ||
| priority-level | ||
| ransomware | ||
| retention | ||
| rsit | ||
| rt_event_status | ||
| runtime-packer | ||
| scrippsco2-fgc | ||
| scrippsco2-fgi | ||
| scrippsco2-sampling-stations | ||
| smart-airports-threats | ||
| stealth_malware | ||
| stix-ttp | ||
| targeted-threat-index | ||
| threatmatch-alert-types | ||
| threatmatch-incident-types | ||
| threatmatch-malware-types | ||
| threatmatch-sectors | ||
| threats-to-dns | ||
| tlp | ||
| tools | ||
| tor | ||
| trust | ||
| type | ||
| use-case-applicability | ||
| veris | ||
| vocabulaire-des-probabilites-estimatives | ||
| workflow | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| LICENSE.md | ||
| MANIFEST.json | ||
| README.md | ||
| jq_all_the_things.sh | ||
| schema.json | ||
| schema_mapping.json | ||
| summary.md | ||
| validate_all.sh | ||
README.md
MISP Taxonomies
MISP Taxonomies is a set of common classification libraries to tag, classify and organise information. Taxonomy allows to express the same vocabulary among a distributed set of users and organisations.
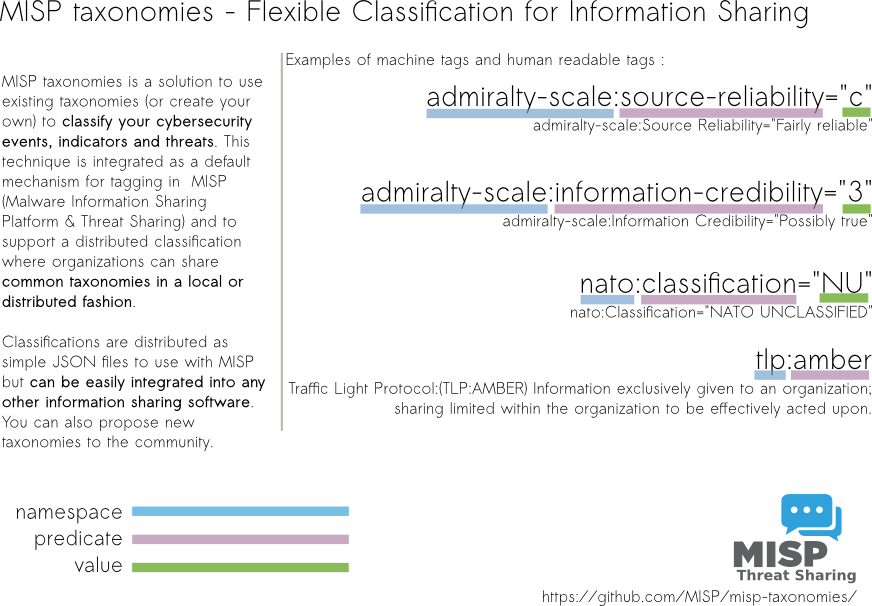
Taxonomies that can be used in MISP (2.4) and other information sharing tool and expressed in Machine Tags (Triple Tags). A machine tag is composed of a namespace (MUST), a predicate (MUST) and an (OPTIONAL) value. Machine tags are often called triple tag due to their format.
The following taxonomies can be used in MISP (as local or distributed tags) or in other tools and software willing to share common taxonomies among security information sharing tools.
The following taxonomies are described:
- access-method
- action-taken
- Admiralty Scale
- adversary - description of an adversary infrastructure
- ais-marking
- analyst-assessment
- binary-class
- CERT-XLM
- CIRCL Taxonomy - Schemes of Classification in Incident Response and Detection
- The CSSA agreed sharing taxonomy
- Collaborative intelligence - Collaborative intelligence support language is a common language to support analysts to perform their analysis to get crowdsourced support when using threat intelligence sharing platform like MISP. The objective of this language is to advance collaborative analysis and to share earlier than later.
- Cryptocurrency Threat - Threats targetting cryptocurrency, based on CipherTrace report.
- Cyber Kill Chain from Lockheed Martin
- The Cyber Threat Framework was developed by the US Government to enable consistent characterization and categorization of cyber threat events, and to identify trends or changes in the activities of cyber adversaries.
- Current Events - List of current events ranging from political to medical matters.
- DE German (DE) Government classification markings (VS)
- DCSO Sharing Taxonomy - DCSO Sharing Taxonomy to classify certain types of MISP events using the DCSO Event Guide
- DHS CIIP Sectors
- Diamond Model for Intrusion Analysis
- Detection Maturity Level
- Domain Name Abuse
- eCSIRT and IntelMQ incident classification
- ENISA ENISA Threat Taxonomy
- Estimative Language Estimative Language (ICD 203)
- EU NIS Critical Infrastructure Operators - EU NIS Critical Infrastructure Operators
- EUCI - EU classified information marking
- Europol Incident - Europol class of incident taxonomy
- Europol Events - Europol type of events taxonomy
- FIRST CSIRT Case classification
- FIRST Information Exchange Policy (IEP) framework
- Information Security Indicators - ETSI GS ISI 001-1 (V1.1.2): ISI Indicators
- Information Security Marking Metadata from DNI (Director of National Intelligence - US)
- Malware classification based on a SANS document
- ms-caro-malware Malware Type and Platform classification based on Microsoft's implementation of the Computer Antivirus Research Organization (CARO) Naming Scheme and Malware Terminology.
- NATO Classification Marking
- Open Threat Taxonomy v1.1 (SANS)
- OSINT Open Source Intelligence - Classification
- Pandemic - Pandemic events
- Ransomware
- runtime-packer - Runtime or software packer used to combine compressed data with the decompression code. The decompression code can add additional obfuscations mechanisms including polymorphic-packer or other o bfuscation techniques. This taxonomy lists all the known or official packer used for legitimate use or for packing malicious binaries.
- STIX-TTP - Represents the behavior or modus operandi of cyber adversaries as normalized in STIX
- Stealth Malware Taxonomy as defined by Joanna Rutkowska
- The Permissible Actions Protocol - or short: PAP - was designed to indicate how the received information can be used.
- Targeted Threat Index is a metric for assigning an overall threat ranking score to email messages that deliver malware to a victim’s computer.
- TLP - Traffic Light Protocol
- Trust - Indicators of Trust
- Type
- Vocabulaire des probabilités estimatives
- Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing VERIS
- Binary Classification safe/malicious binary tagging
- Workflow support language is a common language to support intelligence analysts to perform their analysis on data and information.
- file-type - List of known file types.
- iot - Interbet of Things Taxonomy
Admiralty Scale
The Admiralty Scale (also called the NATO System) is used to rank the reliability of a source and the credibility of an information.
Adversary
An overview and description of the adversary infrastructure.
CIRCL Taxonomy - Schemes of Classification in Incident Response and Detection
CIRCL Taxonomy is a simple scheme for incident classification and area topic where the incident took place.
Cyber Kill Chain from Lockheed Martin
Cyber Kill Chain from Lockheed Martin as described in Intelligence-Driven Computer Network Defense Informed by Analysis of Adversary Campaigns and Intrusion Kill Chains.
Cyber Threat Framework from DNI.gov
The Cyber Threat Framework was developed by the US Government to enable consistent characterization and categorization of cyber threat events, and to identify trends or changes in the activities of cyber adversaries.
DE German (DE) Government classification markings (VS)
Taxonomy for the handling of protectively marked information in MISP with German (DE) Government classification markings (VS).
DHS CIIP Sectors
DHS critical sectors as described in https://www.dhs.gov/critical-infrastructure-sectors.
Diamond Model for Intrusion Analysis
The Diamond Model for Intrusion Analysis, a phase-based model developed by Lockheed Martin, aims to help categorise and identify the stage of an attack as described in http://www.activeresponse.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/diamond.pdf.
Detection Maturity Level
The Detection Maturity Level (DML) model is a capability maturity model for referencing ones maturity in detecting cyber attacks. It's designed for organizations who perform intel-driven detection and response and who put an emphasis on having a mature detection program.
Domain Name Abuse
Taxonomy to tag domain names used for cybercrime. We suggest to use europol-incident(./europol-incident) to tag abuse-activity.
eCSIRT and IntelMQ incident classification
eCSIRT incident classification Appendix C of the eCSIRT EU project including IntelMQ updates.
ENISA ENISA Threat Taxonomy
ENISA Threat Taxonomy - A tool for structuring threat information as published
Estimative Language Estimative Language (ICD 203)
Estimative language - including likelihood or probability of event based on the Intelligence Community Directive 203 (ICD 203) (6.2.(a)).
EU NIS Critical Infrastructure Operators
Market operators and public administrations that must comply to some notifications requirements under EU NIS directive.
EUCI classification
EU classified information (EUCI) means any information or material designated by a EU security classification, the unauthorised disclosure of which could cause varying degrees of prejudice to the interests of the European Union or of one or more of the Member States as described.
Europol Incident
EUROPOL class of incident taxonomy
Europol Events
EUROPOL type of events taxonomy
FIRST CSIRT Case classification
FIRST CSIRT Case Classification.
FIRST Information Exchange Policy (IEP) framework
Information Security Indicators - ETSI GS ISI 001-1 (V1.1.2): ISI Indicators
Information security indicators have been standardized by the ETSI Industrial Specification Group (ISG) ISI. These indicators provide the basis to switch from a qualitative to a quantitative culture in IT Security Scope of measurements: External and internal threats (attempt and success), user's deviant behaviours, nonconformities and/or vulnerabilities (software, configuration, behavioural, general security framework).
Information Security Marking Metadata DNI (Director of National Intelligence - US)
ISM (Information Security Marking Metadata) V13 as described by DNI.gov.
Malware classification
Malware classification based on a SANS whitepaper about malware.
ms-caro-malware Malware Type and Platform classification based on Microsoft's implementation of the Computer Antivirus Research Organization (CARO) Naming Scheme and Malware Terminology.
NATO Classification Marking
Marking of Classified and Unclassified materials as described by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO.
Open Threat Taxonomy v1.1
Open Threat Taxonomy v1.1 base on James Tarala of SANS ref.
STIX-TTP
STIX-TTP exposes a set classification tools that represents the behavior or modus operandi of cyber adversaries as normalized in STIX. TTPs consist of the specific adversary behavior (attack patterns, malware, exploits) exhibited, resources leveraged (tools, infrastructure, personas), information on the victims targeted (who, what or where), relevant ExploitTargets being targeted, intended effects, relevant kill chain phases, handling guidance, source of the TTP information, etc.
Targeted Threat Index is a metric for assigning an overall threat ranking score to email messages that deliver malware to a victim’s computer.
The Targeted Threat Index is a metric for assigning an overall threat ranking score to email messages that deliver malware to a victim’s computer. The TTI metric was first introduced at SecTor 2013 by Seth Hardy as part of the talk “RATastrophe: Monitoring a Malware Menagerie” along with Katie Kleemola and Greg Wiseman. More info about TTI.
The Permissible Actions Protocol - or short: PAP - was designed to indicate how the received information can be used.
The Permissible Actions Protocol - or short: PAP - was designed to indicate how the received information can be used. It's a protocol/taxonomy similar to TLP informing the recipients of information what they can do with the received information.
TLP - Traffic Light Protocol
The Traffic Light Protocol - or short: TLP - was designed with the objective to create a favorable classification scheme for sharing sensitive information while keeping the control over its distribution at the same time.
Trust - Indicators of Trust
The Trust Taxonomy provides a way to use Indicators of Trust within MISP to get insight on data about what can be trusted. Similar to a whitelist but on steroids, leveraging MISP features one would use with Inidicators of Compromise, but to filter out what is known to be good.
Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing VERIS
Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing is a format created by the VERIS community.
Reserved Taxonomy
The following taxonomy namespaces are reserved and used internally to MISP.
- galaxy mapping taxonomy with cluster:element:"value".
Documentation
A documentation of the taxonomies is generated automatically from the taxonomies description and available in PDF and HTML.
How to contribute your taxonomy?
It is quite easy. Create a JSON file describing your taxonomy as triple tags (e.g. check an existing one like Admiralty Scale), create a directory matching your name space, put your machinetag file in the directory and pull your request. That's it. Everyone can benefit from your taxonomy and can be automatically enabled in information sharing tools like MISP.
For more information, "Information Sharing and Taxonomies Practical Classification of Threat Indicators using MISP" presentation given to the last MISP training in Luxembourg.
How to add your private taxonomy to MISP
$ cd /var/www/MISP/app/files/taxonomies/
$ mkdir privatetaxonomy
$ cd privatetaxonomy
$ vi machinetag.json
Create a JSON file describing your taxonomy as triple tags.
Once you are happy with your file go to MISP Web GUI taxonomies/index and update the taxonomies, the newly created taxonomy should be visible, now you need to activate the tags within your taxonomy.
MISP Taxonomies
Tools
machinetag.py is a parsing tool to dump taxonomies expressed in Machine Tags (Triple Tags) and list all valid tags from a specific taxonomy.
% cd tools
% python machinetag.py
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="a"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="b"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="c"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="d"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="e"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="f"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="1"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="2"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="3"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="4"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="5"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="6"
...
Library
- PyTaxonomies is a Python module to use easily the MISP Taxonomies.
License
The MISP taxonomies (JSON files) are dual-licensed under:
- CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0) - Public Domain Dedication.
or
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 Alexandre Dulaunoy - a@foo.be
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 CIRCL - Computer Incident Response Center Luxembourg
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 Andras Iklody
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 Raphael Vinot
Copyright (c) 2016-2021 Various contributors to MISP Project
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT,
INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE
OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
If a specific author of a taxonomy wants to license it under a different license, a pull request can be requested.