53 KiB
MISP Taxonomies
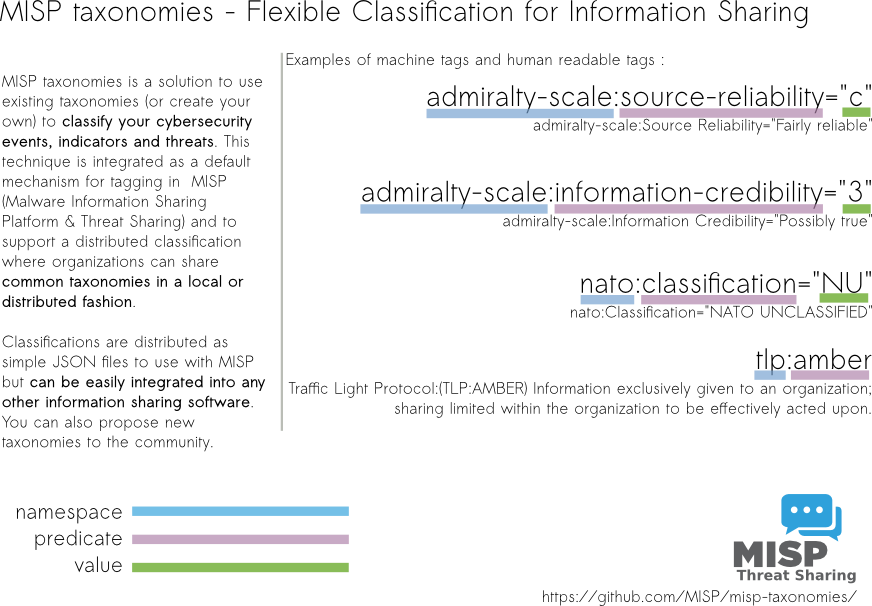
MISP Taxonomies is a set of common classification libraries to tag, classify and organise information. Taxonomy allows to express the same vocabulary among a distributed set of users and organisations.
Taxonomies that can be used in MISP and other information sharing tool, are expressed in Machine Tags (Triple Tags). A machine tag is composed of a namespace (MUST), a predicate (MUST) and an (OPTIONAL) value. Machine tags are often called triple tag due to their format.
The following taxonomies can be used in MISP (as local or distributed tags) or in other tools and software willing to share common taxonomies among security information sharing tools.
List of available taxonomies
CERT-XLM
CERT-XLM : CERT-XLM Security Incident Classification. Overview
DFRLab-dichotomies-of-disinformation
DFRLab-dichotomies-of-disinformation : DFRLab Dichotomies of Disinformation. Overview
DML
DML : The Detection Maturity Level (DML) model is a capability maturity model for referencing ones maturity in detecting cyber attacks. It's designed for organizations who perform intel-driven detection and response and who put an emphasis on having a mature detection program. Overview
GrayZone
GrayZone : Gray Zone of Active defense includes all elements which lay between reactive defense elements and offensive operations. It does fill the gray spot between them. Taxo may be used for active defense planning or modeling. Overview
PAP
PAP : The Permissible Actions Protocol - or short: PAP - was designed to indicate how the received information can be used. Overview
access-method
access-method : The access method used to remotely access a system. Overview
accessnow
accessnow : Access Now classification to classify an issue (such as security, human rights, youth rights). Overview
action-taken
action-taken : Action taken in the case of a security incident (CSIRT perspective). Overview
admiralty-scale
admiralty-scale : The Admiralty Scale or Ranking (also called the NATO System) is used to rank the reliability of a source and the credibility of an information. Reference based on FM 2-22.3 (FM 34-52) HUMAN INTELLIGENCE COLLECTOR OPERATIONS and NATO documents. Overview
adversary
adversary : An overview and description of the adversary infrastructure Overview
ais-marking
ais-marking : The AIS Marking Schema implementation is maintained by the National Cybersecurity and Communication Integration Center (NCCIC) of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Overview
analyst-assessment
analyst-assessment : A series of assessment predicates describing the analyst capabilities to perform analysis. These assessment can be assigned by the analyst him/herself or by another party evaluating the analyst. Overview
approved-category-of-action
approved-category-of-action : A pre-approved category of action for indicators being shared with partners (MIMIC). Overview
artificial-satellites
artificial-satellites : This taxonomy was designed to describe artificial satellites Overview
aviation
aviation : A taxonomy describing security threats or incidents against the aviation sector. Overview
binary-class
binary-class : Custom taxonomy for types of binary file. Overview
cccs
cccs : Internal taxonomy for CCCS. Overview
circl
circl : CIRCL Taxonomy - Schemes of Classification in Incident Response and Detection Overview
cnsd
cnsd : La presente taxonomia es la primera versión disponible para el Centro Nacional de Seguridad Digital del Perú. Overview
coa
coa : Course of action taken within organization to discover, detect, deny, disrupt, degrade, deceive and/or destroy an attack. Overview
collaborative-intelligence
collaborative-intelligence : Collaborative intelligence support language is a common language to support analysts to perform their analysis to get crowdsourced support when using threat intelligence sharing platform like MISP. The objective of this language is to advance collaborative analysis and to share earlier than later. Overview
common-taxonomy
common-taxonomy : Common Taxonomy for Law enforcement and CSIRTs Overview
copine-scale
copine-scale : The COPINE Scale is a rating system created in Ireland and used in the United Kingdom to categorise the severity of images of child sex abuse. The scale was developed by staff at the COPINE (Combating Paedophile Information Networks in Europe) project. The COPINE Project was founded in 1997, and is based in the Department of Applied Psychology, University College Cork, Ireland. Overview
course-of-action
course-of-action : A Course Of Action analysis considers six potential courses of action for the development of a cyber security capability. Overview
crowdsec
crowdsec : The Crowdsec behaviors and classifications taxonomy is the list of taxonomies used in Crowdsec to describe the behaviors and classifications of an IP address. The behaviors are a list of attack categories for which a given IP address was reported, where the classifications describe a list of categories associated to an IP address and, when applicable, a list of false positive categories. Overview
cryptocurrency-threat
cryptocurrency-threat : Threats targetting cryptocurrency, based on CipherTrace report. Overview
csirt-americas
csirt-americas : Taxonomía CSIRT Américas. Overview
csirt_case_classification
csirt_case_classification : It is critical that the CSIRT provide consistent and timely response to the customer, and that sensitive information is handled appropriately. This document provides the guidelines needed for CSIRT Incident Managers (IM) to classify the case category, criticality level, and sensitivity level for each CSIRT case. This information will be entered into the Incident Tracking System (ITS) when a case is created. Consistent case classification is required for the CSIRT to provide accurate reporting to management on a regular basis. In addition, the classifications will provide CSIRT IM’s with proper case handling procedures and will form the basis of SLA’s between the CSIRT and other Company departments. Overview
cssa
cssa : The CSSA agreed sharing taxonomy. Overview
cti
cti : Cyber Threat Intelligence cycle to control workflow state of your process. Overview
current-event
current-event : Current events - Schemes of Classification in Incident Response and Detection Overview
cyber-threat-framework
cyber-threat-framework : Cyber Threat Framework was developed by the US Government to enable consistent characterization and categorization of cyber threat events, and to identify trends or changes in the activities of cyber adversaries. https://www.dni.gov/index.php/cyber-threat-framework Overview
cycat
cycat : Taxonomy used by CyCAT, the Universal Cybersecurity Resource Catalogue, to categorize the namespaces it supports and uses. Overview
cytomic-orion
cytomic-orion : Taxonomy to describe desired actions for Cytomic Orion Overview
dark-web
dark-web : Criminal motivation on the dark web: A categorisation model for law enforcement. ref: Janis Dalins, Campbell Wilson, Mark Carman. Taxonomy updated by MISP Project Overview
data-classification
data-classification : Data classification for data potentially at risk of exfiltration based on table 2.1 of Solving Cyber Risk book. Overview
dcso-sharing
dcso-sharing : Taxonomy defined in the DCSO MISP Event Guide. It provides guidance for the creation and consumption of MISP events in a way that minimises the extra effort for the sending party, while enhancing the usefulness for receiving parties. Overview
ddos
ddos : Distributed Denial of Service - or short: DDoS - taxonomy supports the description of Denial of Service attacks and especially the types they belong too. Overview
de-vs
de-vs : German (DE) Government classification markings (VS). Overview
death-possibilities
death-possibilities : Taxonomy of Death Possibilities Overview
deception
deception : Deception is an important component of information operations, valuable for both offense and defense. Overview
dga
dga : A taxonomy to describe domain-generation algorithms often called DGA. Ref: A Comprehensive Measurement Study of Domain Generating Malware Daniel Plohmann and others. Overview
dhs-ciip-sectors
dhs-ciip-sectors : DHS critical sectors as in https://www.dhs.gov/critical-infrastructure-sectors Overview
diamond-model
diamond-model : The Diamond Model for Intrusion Analysis establishes the basic atomic element of any intrusion activity, the event, composed of four core features: adversary, infrastructure, capability, and victim. Overview
diamond-model-for-influence-operations
diamond-model-for-influence-operations : The diamond model for influence operations analysis is a framework that leads analysts and researchers toward a comprehensive understanding of a malign influence campaign by addressing the socio-political, technical, and psychological aspects of the campaign. The diamond model for influence operations analysis consists of 5 components: 4 corners and a core element. The 4 corners are divided into 2 axes: influencer and audience on the socio-political axis, capabilities and infrastructure on the technical axis. Narrative makes up the core of the diamond. Overview
dni-ism
dni-ism : A subset of Information Security Marking Metadata ISM as required by Executive Order (EO) 13526. As described by DNI.gov as Data Encoding Specifications for Information Security Marking Metadata in Controlled Vocabulary Enumeration Values for ISM Overview
domain-abuse
domain-abuse : Domain Name Abuse - taxonomy to tag domain names used for cybercrime. Overview
drugs
drugs : A taxonomy based on the superclass and class of drugs. Based on https://www.drugbank.ca/releases/latest Overview
economical-impact
economical-impact : Economical impact is a taxonomy to describe the financial impact as positive or negative gain to the tagged information (e.g. data exfiltration loss, a positive gain for an adversary). Overview
ecsirt
ecsirt : Incident Classification by the ecsirt.net version mkVI of 31 March 2015 enriched with IntelMQ taxonomy-type mapping. Overview
enisa
enisa : The present threat taxonomy is an initial version that has been developed on the basis of available ENISA material. This material has been used as an ENISA-internal structuring aid for information collection and threat consolidation purposes. It emerged in the time period 2012-2015. Overview
estimative-language
estimative-language : Estimative language to describe quality and credibility of underlying sources, data, and methodologies based Intelligence Community Directive 203 (ICD 203) and JP 2-0, Joint Intelligence Overview
eu-marketop-and-publicadmin
eu-marketop-and-publicadmin : Market operators and public administrations that must comply to some notifications requirements under EU NIS directive Overview
eu-nis-sector-and-subsectors
eu-nis-sector-and-subsectors : Sectors, subsectors, and digital services as identified by the NIS Directive Overview
euci
euci : EU classified information (EUCI) means any information or material designated by a EU security classification, the unauthorised disclosure of which could cause varying degrees of prejudice to the interests of the European Union or of one or more of the Member States. Overview
europol-event
europol-event : This taxonomy was designed to describe the type of events Overview
europol-incident
europol-incident : This taxonomy was designed to describe the type of incidents by class. Overview
event-assessment
event-assessment : A series of assessment predicates describing the event assessment performed to make judgement(s) under a certain level of uncertainty. Overview
event-classification
event-classification : Classification of events as seen in tools such as RT/IR, MISP and other Overview
exercise
exercise : Exercise is a taxonomy to describe if the information is part of one or more cyber or crisis exercise. Overview
extended-event
extended-event : Reasons why an event has been extended. This taxonomy must be used on the extended event. The competitive analysis aspect is from Psychology of Intelligence Analysis by Richard J. Heuer, Jr. ref:http://www.foo.be/docs/intelligence/PsychofIntelNew.pdf Overview
failure-mode-in-machine-learning
failure-mode-in-machine-learning : The purpose of this taxonomy is to jointly tabulate both the of these failure modes in a single place. Intentional failures wherein the failure is caused by an active adversary attempting to subvert the system to attain her goals – either to misclassify the result, infer private training data, or to steal the underlying algorithm. Unintentional failures wherein the failure is because an ML system produces a formally correct but completely unsafe outcome. Overview
false-positive
false-positive : This taxonomy aims to ballpark the expected amount of false positives. Overview
file-type
file-type : List of known file types. Overview
financial
financial : Financial taxonomy to describe financial services, infrastructure and financial scope. Overview
flesch-reading-ease
flesch-reading-ease : Flesch Reading Ease is a revised system for determining the comprehension difficulty of written material. The scoring of the flesh score can have a maximum of 121.22 and there is no limit on how low a score can be (negative score are valid). Overview
fpf
fpf : The Future of Privacy Forum (FPF) visual guide to practical de-identification taxonomy is used to evaluate the degree of identifiability of personal data and the types of pseudonymous data, de-identified data and anonymous data. The work of FPF is licensed under a creative commons attribution 4.0 international license. Overview
fr-classif
fr-classif : French gov information classification system Overview
gdpr
gdpr : Taxonomy related to the REGULATION (EU) 2016/679 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL on the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data, and repealing Directive 95/46/EC (General Data Protection Regulation) Overview
gea-nz-activities
gea-nz-activities : Information needed to track or monitor moments, periods or events that occur over time. This type of information is focused on occurrences that must be tracked for business reasons or represent a specific point in the evolution of ‘The Business’. Overview
gea-nz-entities
gea-nz-entities : Information relating to instances of entities or things. Overview
gea-nz-motivators
gea-nz-motivators : Information relating to authority or governance. Overview
gsma-attack-category
gsma-attack-category : Taxonomy used by GSMA for their information sharing program with telco describing the attack categories Overview
gsma-fraud
gsma-fraud : Taxonomy used by GSMA for their information sharing program with telco describing the various aspects of fraud Overview
gsma-network-technology
gsma-network-technology : Taxonomy used by GSMA for their information sharing program with telco describing the types of infrastructure. WiP Overview
honeypot-basic
honeypot-basic : Updated (CIRCL, Seamus Dowling and EURECOM) from Christian Seifert, Ian Welch, Peter Komisarczuk, ‘Taxonomy of Honeypots’, Technical Report CS-TR-06/12, VICTORIA UNIVERSITY OF WELLINGTON, School of Mathematical and Computing Sciences, June 2006, http://www.mcs.vuw.ac.nz/comp/Publications/archive/CS-TR-06/CS-TR-06-12.pdf Overview
ics
ics : FIRST.ORG CTI SIG - MISP Proposal for ICS/OT Threat Attribution (IOC) Project Overview
iep
iep : Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) Information Exchange Policy (IEP) framework Overview
iep2-policy
iep2-policy : Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) Information Exchange Policy (IEP) v2.0 Policy Overview
iep2-reference
iep2-reference : Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) Information Exchange Policy (IEP) v2.0 Reference Overview
ifx-vetting
ifx-vetting : The IFX taxonomy is used to categorise information (MISP events and attributes) to aid in the intelligence vetting process Overview
incident-disposition
incident-disposition : How an incident is classified in its process to be resolved. The taxonomy is inspired from NASA Incident Response and Management Handbook. https://www.nasa.gov/pdf/589502main_ITS-HBK-2810.09-02%20%5bNASA%20Information%20Security%20Incident%20Management%5d.pdf#page=9 Overview
infoleak
infoleak : A taxonomy describing information leaks and especially information classified as being potentially leaked. The taxonomy is based on the work by CIRCL on the AIL framework. The taxonomy aim is to be used at large to improve classification of leaked information. Overview
information-security-data-source
information-security-data-source : Taxonomy to classify the information security data sources. Overview
information-security-indicators
information-security-indicators : A full set of operational indicators for organizations to use to benchmark their security posture. Overview
interactive-cyber-training-audience
interactive-cyber-training-audience : Describes the target of cyber training and education. Overview
interactive-cyber-training-technical-setup
interactive-cyber-training-technical-setup : The technical setup consists of environment structure, deployment, and orchestration. Overview
interactive-cyber-training-training-environment
interactive-cyber-training-training-environment : The training environment details the environment around the training, consisting of training type and scenario. Overview
interactive-cyber-training-training-setup
interactive-cyber-training-training-setup : The training setup further describes the training itself with the scoring, roles, the training mode as well as the customization level. Overview
interception-method
interception-method : The interception method used to intercept traffic. Overview
ioc
ioc : An IOC classification to facilitate automation of malicious and non malicious artifacts Overview
iot
iot : Internet of Things taxonomy, based on IOT UK report https://iotuk.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/IOT-Taxonomy-Report.pdf Overview
kill-chain
kill-chain : The Cyber Kill Chain, a phase-based model developed by Lockheed Martin, aims to help categorise and identify the stage of an attack. Overview
maec-delivery-vectors
maec-delivery-vectors : Vectors used to deliver malware based on MAEC 5.0 Overview
maec-malware-behavior
maec-malware-behavior : Malware behaviours based on MAEC 5.0 Overview
maec-malware-capabilities
maec-malware-capabilities : Malware Capabilities based on MAEC 5.0 Overview
maec-malware-obfuscation-methods
maec-malware-obfuscation-methods : Obfuscation methods used by malware based on MAEC 5.0 Overview
malware_classification
malware_classification : Classification based on different categories. Based on https://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers/incident/malware-101-viruses-32848 Overview
misinformation-website-label
misinformation-website-label : classification for the identification of type of misinformation among websites. Source:False, Misleading, Clickbait-y, and/or Satirical News Sources by Melissa Zimdars 2019 Overview
misp
misp : MISP taxonomy to infer with MISP behavior or operation. Overview
misp-workflow
misp-workflow : MISP workflow taxonomy to support result of workflow execution. Overview
monarc-threat
monarc-threat : MONARC Threats Taxonomy Overview
ms-caro-malware
ms-caro-malware : Malware Type and Platform classification based on Microsoft's implementation of the Computer Antivirus Research Organization (CARO) Naming Scheme and Malware Terminology. Based on https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/portal/mmpc/shared/malwarenaming.aspx, https://www.microsoft.com/security/portal/mmpc/shared/glossary.aspx, https://www.microsoft.com/security/portal/mmpc/shared/objectivecriteria.aspx, and http://www.caro.org/definitions/index.html. Malware families are extracted from Microsoft SIRs since 2008 based on https://www.microsoft.com/security/sir/archive/default.aspx and https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/portal/threat/threats.aspx. Note that SIRs do NOT include all Microsoft malware families. Overview
ms-caro-malware-full
ms-caro-malware-full : Malware Type and Platform classification based on Microsoft's implementation of the Computer Antivirus Research Organization (CARO) Naming Scheme and Malware Terminology. Based on https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/portal/mmpc/shared/malwarenaming.aspx, https://www.microsoft.com/security/portal/mmpc/shared/glossary.aspx, https://www.microsoft.com/security/portal/mmpc/shared/objectivecriteria.aspx, and http://www.caro.org/definitions/index.html. Malware families are extracted from Microsoft SIRs since 2008 based on https://www.microsoft.com/security/sir/archive/default.aspx and https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/portal/threat/threats.aspx. Note that SIRs do NOT include all Microsoft malware families. Overview
mwdb
mwdb : Malware Database (mwdb) Taxonomy - Tags used across the platform Overview
nato
nato : NATO classification markings. Overview
nis
nis : The taxonomy is meant for large scale cybersecurity incidents, as mentioned in the Commission Recommendation of 13 September 2017, also known as the blueprint. It has two core parts: The nature of the incident, i.e. the underlying cause, that triggered the incident, and the impact of the incident, i.e. the impact on services, in which sector(s) of economy and society. Overview
nis2
nis2 : The taxonomy is meant for large scale cybersecurity incidents, as mentioned in the Commission Recommendation of 13 May 2022, also known as the provisional agreement. It has two core parts: The nature of the incident, i.e. the underlying cause, that triggered the incident, and the impact of the incident, i.e. the impact on services, in which sector(s) of economy and society. Overview
open_threat
open_threat : Open Threat Taxonomy v1.1 base on James Tarala of SANS http://www.auditscripts.com/resources/open_threat_taxonomy_v1.1a.pdf, https://files.sans.org/summit/Threat_Hunting_Incident_Response_Summit_2016/PDFs/Using-Open-Tools-to-Convert-Threat-Intelligence-into-Practical-Defenses-James-Tarala-SANS-Institute.pdf, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5rdGOOFC_yE, and https://www.rsaconference.com/writable/presentations/file_upload/str-r04_using-an-open-source-threat-model-for-prioritized-defense-final.pdf Overview
osint
osint : Open Source Intelligence - Classification (MISP taxonomies) Overview
pandemic
passivetotal
passivetotal : Tags from RiskIQ's PassiveTotal service Overview
pentest
pentest : Penetration test (pentest) classification. Overview
phishing
phishing : Taxonomy to classify phishing attacks including techniques, collection mechanisms and analysis status. Overview
poison-taxonomy
poison-taxonomy : Non-exhaustive taxonomy of natural poison Overview
political-spectrum
political-spectrum : A political spectrum is a system to characterize and classify different political positions in relation to one another. Overview
priority-level
priority-level : After an incident is scored, it is assigned a priority level. The six levels listed below are aligned with NCCIC, DHS, and the CISS to help provide a common lexicon when discussing incidents. This priority assignment drives NCCIC urgency, pre-approved incident response offerings, reporting requirements, and recommendations for leadership escalation. Generally, incident priority distribution should follow a similar pattern to the graph below. Based on https://www.us-cert.gov/NCCIC-Cyber-Incident-Scoring-System. Overview
pyoti
pyoti : PyOTI automated enrichment schemes for point in time classification of indicators. Overview
ransomware
ransomware : Ransomware is used to define ransomware types and the elements that compose them. Overview
ransomware-roles
ransomware-roles : The seven roles seen in most ransomware incidents. Overview
retention
retention : Add a retenion time to events to automatically remove the IDS-flag on ip-dst or ip-src attributes. We calculate the time elapsed based on the date of the event. Supported time units are: d(ays), w(eeks), m(onths), y(ears). The numerical_value is just for sorting in the web-interface and is not used for calculations. Overview
rsit
rsit : Reference Security Incident Classification Taxonomy Overview
rt_event_status
rt_event_status : Status of events used in Request Tracker. Overview
runtime-packer
runtime-packer : Runtime or software packer used to combine compressed or encrypted data with the decompression or decryption code. This code can add additional obfuscations mechanisms including polymorphic-packer or other obfuscation techniques. This taxonomy lists all the known or official packer used for legitimate use or for packing malicious binaries. Overview
scrippsco2-fgc
scrippsco2-fgc : Flags describing the sample Overview
scrippsco2-fgi
scrippsco2-fgi : Flags describing the sample for isotopic data (C14, O18) Overview
scrippsco2-sampling-stations
scrippsco2-sampling-stations : Sampling stations of the Scripps CO2 Program Overview
sentinel-threattype
sentinel-threattype : Sentinel indicator threat types. Overview
smart-airports-threats
smart-airports-threats : Threat taxonomy in the scope of securing smart airports by ENISA. https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/securing-smart-airports Overview
social-engineering-attack-vectors
social-engineering-attack-vectors : Attack vectors used in social engineering as described in 'A Taxonomy of Social Engineering Defense Mechanisms' by Dalal Alharthi and others. Overview
state-responsibility
state-responsibility : A spectrum of state responsibility to more directly tie the goals of attribution to the needs of policymakers. Overview
stealth_malware
stealth_malware : Classification based on malware stealth techniques. Described in https://vxheaven.org/lib/pdf/Introducing%20Stealth%20Malware%20Taxonomy.pdf Overview
stix-ttp
stix-ttp : TTPs are representations of the behavior or modus operandi of cyber adversaries. Overview
targeted-threat-index
targeted-threat-index : The Targeted Threat Index is a metric for assigning an overall threat ranking score to email messages that deliver malware to a victim’s computer. The TTI metric was first introduced at SecTor 2013 by Seth Hardy as part of the talk “RATastrophe: Monitoring a Malware Menagerie” along with Katie Kleemola and Greg Wiseman. Overview
thales_group
thales_group : Thales Group Taxonomy - was designed with the aim of enabling desired sharing and preventing unwanted sharing between Thales Group security communities. Overview
threatmatch
threatmatch : The ThreatMatch Sectors, Incident types, Malware types and Alert types are applicable for any ThreatMatch instances and should be used for all CIISI and TIBER Projects. Overview
threats-to-dns
threats-to-dns : An overview of some of the known attacks related to DNS as described by Torabi, S., Boukhtouta, A., Assi, C., & Debbabi, M. (2018) in Detecting Internet Abuse by Analyzing Passive DNS Traffic: A Survey of Implemented Systems. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 1–1. doi:10.1109/comst.2018.2849614 Overview
tlp
tlp : The Traffic Light Protocol (TLP) (v2.0) was created to facilitate greater sharing of potentially sensitive information and more effective collaboration. Information sharing happens from an information source, towards one or more recipients. TLP is a set of four standard labels (a fifth label is included in amber to limit the diffusion) used to indicate the sharing boundaries to be applied by the recipients. Only labels listed in this standard are considered valid by FIRST. This taxonomy includes additional labels for backward compatibility which are no more validated by FIRST SIG. Overview
tor
tor : Taxonomy to describe Tor network infrastructure Overview
trust
trust : The Indicator of Trust provides insight about data on what can be trusted and known as a good actor. Similar to a whitelist but on steroids, reusing features one would use with Indicators of Compromise, but to filter out what is known to be good. Overview
type
type : Taxonomy to describe different types of intelligence gathering discipline which can be described the origin of intelligence. Overview
unified-kill-chain
unified-kill-chain : The Unified Kill Chain is a refinement to the Kill Chain. Overview
use-case-applicability
use-case-applicability : The Use Case Applicability categories reflect standard resolution categories, to clearly display alerting rule configuration problems. Overview
veris
veris : Vocabulary for Event Recording and Incident Sharing (VERIS) Overview
vmray
vmray : VMRay taxonomies to map VMRay Thread Identifier scores and artifacts. Overview
vocabulaire-des-probabilites-estimatives
vocabulaire-des-probabilites-estimatives : Ce vocabulaire attribue des valeurs en pourcentage à certains énoncés de probabilité Overview
workflow
workflow : Workflow support language is a common language to support intelligence analysts to perform their analysis on data and information. Overview
Reserved Taxonomy
The following taxonomy namespaces are reserved and used internally to MISP.
- galaxy mapping taxonomy with cluster:element:"value".
Documentation
A documentation of the taxonomies is generated automatically from the taxonomies description and available in PDF and HTML.
How to contribute your taxonomy?
It is quite easy. Create a JSON file describing your taxonomy as triple tags (e.g. check an existing one like Admiralty Scale), create a directory matching your name space, put your machinetag file in the directory and pull your request. That's it. Everyone can benefit from your taxonomy and can be automatically enabled in information sharing tools like MISP.
For more information, "Information Sharing and Taxonomies Practical Classification of Threat Indicators using MISP" presentation given to the last MISP training in Luxembourg.
How to add your private taxonomy to MISP
$ cd /var/www/MISP/app/files/taxonomies/
$ mkdir privatetaxonomy
$ cd privatetaxonomy
$ vi machinetag.json
Create a JSON file describing your taxonomy as triple tags.
Once you are happy with your file go to MISP Web GUI taxonomies/index and update the taxonomies, the newly created taxonomy should be visible, now you need to activate the tags within your taxonomy.
MISP Taxonomies
Tools
machinetag.py is a parsing tool to dump taxonomies expressed in Machine Tags (Triple Tags) and list all valid tags from a specific taxonomy.
% cd tools
% python machinetag.py
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="a"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="b"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="c"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="d"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="e"
admiralty-scale:source-reliability="f"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="1"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="2"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="3"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="4"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="5"
admiralty-scale:information-credibility="6"
...
Library
- PyTaxonomies is a Python module to use easily the MISP Taxonomies.
License
The MISP taxonomies (JSON files) are dual-licensed under:
- CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0) - Public Domain Dedication.
or
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 Alexandre Dulaunoy - a@foo.be
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 CIRCL - Computer Incident Response Center Luxembourg
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 Andras Iklody
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 Raphael Vinot
Copyright (c) 2016-2021 Various contributors to MISP Project
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT,
INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE
OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
If a specific author of a taxonomy wants to license it under a different license, a pull request can be requested.