9.7 KiB
Problem statement
MISP being a P2P system, various users and organisations are sharing data, sometimes without even knowing each others. While having access to a lot of information is extremelly benificial for all parties, it, however, also induces challenges to deal with.
In this blogpost, we will mainly discuss about information quality and freshness, other issues like trust, use-cases, interests, etc. are partially taken into account but will not be presented. Nevertheless, these concepts are examined in this paper along with a detailed explanation of the solution we've choosen to tackle these issues.
Our main objective is to provide users a simple yet customizable system to automatically (or manually) mark an Indicator Of Compromise (or more generic, an Attribute) as expired.
Before getting started to show how the model presented in the paper is implemented in MISP, we first need to have a look at some concepts needed to better understand how components are working and tied together.
The (potentially) annoying bits of theory
The solution currently supported in MISP is based on two components: base_score and score. The idea is to have an initial fixed value called base_score taking into account the quality of an indicator; and a time-dependant score, which decreases the more time passes.
A simplified version would be something like this:
score = base_score * P
Where P is composed of parameters:
lifetime: The lifetime of the IOC or the time at which the score of the Attribute's score will be 0decay_speed: The speed at which the decay happens or the speed at which an Attribute will loose score
⚠ It should be noted that everytime a Sightings is added to an Attribute, the score is refresh to the base_score and a new decay is initiated from that point.
Polynomial Decaying Model built-in in MISP
We still have to see how the base_score is actually computed. In the built-in version of the Decaying Model in MISP, the base_score is computed from the Taxonomies and some weigths. Weights are a mean to prioritize extracted numerical_values from Taxonomies over others.
To give the intuition of how the base_score computation works, let's look at two examples. In these examples, the two Taxonomies used are
phishing and admiralty-scale. Both of them contain Tags that have a numerical_value associated to them:
 ,
, numerical_value = 100 ,
, numerical_value = 25 ,
, numerical_value = 75
So, if an Attribute only have one Tag attached, let's say admiralty-scale:source-reliability="Completely reliable", the base_score would be:
base_score = 100
Weights come into action when multiple Tags are attached to an Attribute. To make things a bit easier, let's suppose that both Taxonomies should have the same importance in regards to the Attribute's score. Thus, the total weigth (100) will be shared, assigning both Taxonomy a weight of 50.
admiralty-scale = 50
phishing = 50
---------------------
sum 100
If an Attribute has the Tags  and
and  attached, the computation steps would look like this:
attached, the computation steps would look like this:
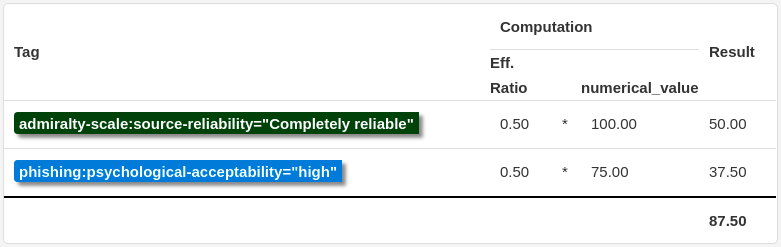
Thus, the base_score of this Attribute will be 87.50.
Short tutorial
Now that we've seen the basic concepts, let's have a look at how MISP implents these components. For these examples, we are using the default phishing model model on a test Event.
Practical integration in MISP
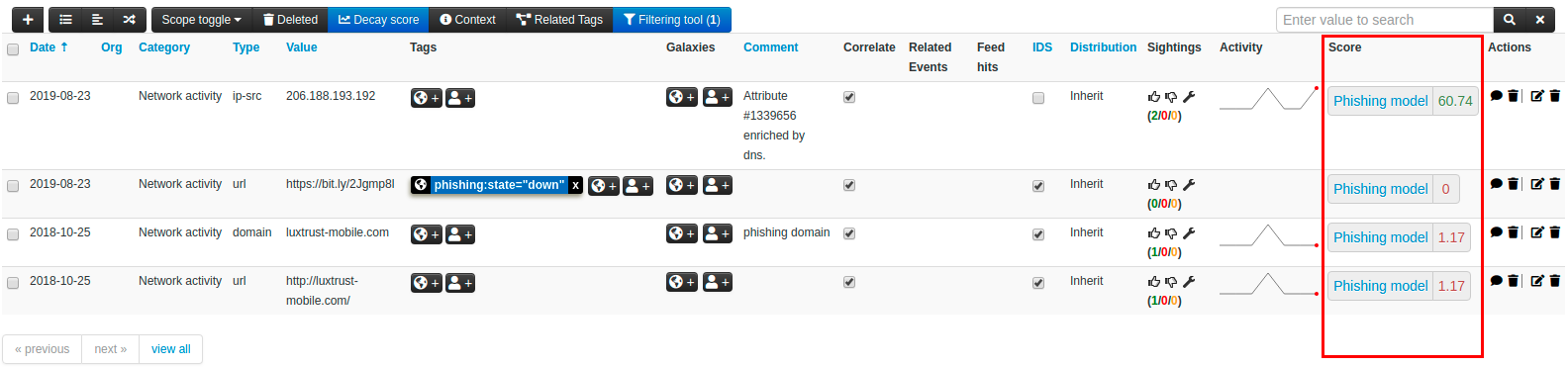
Endpoint: events/view
At the Event level, a new filtering button has been added to attach the real-time computed score of any Attributes that has been mapped to a Model.
Endpoint: attribute/restSearch
The attribute/restSearch endpoint has been updated and now supports four new parameters to filter out expired Attributes or play with the different available models.
includeDecayScore[bool]: Attach the real-time computedscoreof the Attribute along with Model(s) informationsexcludeDecayed[bool]: Filter out all expired IOCdecayingModel[list]: List of Model(s), which will be attached to the AttributemodelOverrides[dict]: JSON that can be used to on-the-fly modify Model(s) parameters
Example
// attribute/restSearch query that gets every `ip-src` attributes being tagged with tlp or phishing,
// not being expired,
// with a overriden model threshold of 30 for the two models with id 84 and 12.
{
"type": "ip-src",
"tags": ["tlp:%","phishing:%"],
"includeDecayScore": 1,
"excludeDecayed": 1,
"modelOverrides": {
"threshold": 30
}
"decayingModel": [84, 12],
}
Default and Custom Models
In MISP, Some Decaying Models called Default Models will be supplied by default. Similarly to Taxonomies, Galaxies or misp-objects, Decaying Models will have their own repository and will have the possibility to be updated directly from the UI via a single click. Default Models are available to everyone, meaning that they can been viewed and customized by any users having a presence on the MISP instance.
Custom Models are user-defined models that are shared to other users. However, if desired, they can be hidden by turning off the sharing flag, similarly to the Tag Collection feature.
Decaying Fine Tuning Tool: Setting parameters and mapping model to Attribute types
When creating a new Decaying Model, setting a parameters and viewing its impact should be as easy and straighforward as possible. To do so, few widgets are shipped with the latest version of MISP.
Customizing lifetime and decay speed parameters
Setting the base_score: Customizing Taxonomies' weigth
Viewing scores and Simulating the model
Developer perspective: Creating a model using a different algorithm
The Built-in Polynomial Decaying Model implemented in MISP allows any user to customize various components to achieve fine-grained decay behaviors. Still, it is possible that our model doesn't encompass your specific use-case. Thanks to the implemented architecture, any other formulas or algorithms can be added and used in a straightforward way.
Steps to create a new decay algorithm:
- Create a new file
$filenameinapp/Model/DecayingModelsFormulas/ - Extend the Base class
DecayingModelBase - Implement the two functions
computeScoreandisDecayedwith you own formula/algorithm - Create a Model and set the
formulafield to$filename
<?php
include_once 'Base.php';
class Polynomial extends DecayingModelBase
{
public const DESCRIPTION = 'The description of your new decaying algorithm';
public function computeScore($model, $attribute, $base_score, $elapsed_time)
{
// algorithm returning a numerical score
}
public function isDecayed($model, $attribute, $score)
{
// algorithm returning a boolean stating if the attribute is expired or not
}
}
?>
Outcomes
Evaluating quality and freshness of IOCs is a problem commonly found in Threat Intelligence Platforms. We tried to solve it using a simple yet customizable system.
Upon release, MISP will be shipped with few models that could fit most use-cases. Still, we are eagerly waiting for contributions, fine-tunings or feedbacks from users. This would opens up plenty of opportunities includings improved Models' precision, parameters tweaking or even integration of machine learning as a new Model algorithm.
Furthermore, we are not done yet! There are already improvements cooking in the MISP-Project oven,
- Integration of
False PositiveandExpirationSightings - Formula tweakings to provide better control on how to reset the
base_scoreonce a Sighting is created - Per-user Taxonomies'
numerical_valueoverrides - Weights on Tag's predicate level